"We are now implementing strategies that intend to increase the current below-World Health Organization [WHO] standard number of medical doctors and retaining them in public hospitals," Tedros Adhanom, Ethiopia's minister of health, told IRIN.
"We have now reached an enrolment rate of more than 3,100," he said. The rate of enrolment in the country's medical schools has increased tenfold from 2005, when it was below 300.
"In the next two, three years, it could go to six and eight thousand," said the minister, adding that once these students start to graduate, the problem regarding shortage of physicians in the country "will [have] considerably stabilized".
While WHO recommends countries have a minimum of one doctor per 10,000 people, Ethiopia has fewer than a fifth of that ratio, compared to a regional average of 2.2 physicians per 10,000 people.
"We have not [supplied] enough doctors despite the high demand," Tedros told IRIN.
A draft of the country's Human Resource for Health Strategic Plan shows an intended increase in the number of physicians to 1 per 5,000 people by 2020. The plan seems on course, with a report presented to parliament in May revealing 2,628 students had been enrolled in 22 universities over the previous nine months. Currently fewer than 200 doctors graduate annually.
But once the new students start to graduate, "We can succeed in easing the problem significantly within three to four years," the minister said. "Afterwards, we can also have more doctors that specialize in several sub-health fields."
Questions over quality
With the strong emphasis on health personnel numbers, experts have expressed concerns about the quality of medical education available.
"Of course, whenever emphasis is given to numbers, quality is compromised," said Milliard Derebew, a medical professor at Addis Ababa University. "Due attention should be given to quality as well," he said.
| Read more |
Through the Medical Education Partnership Initiative (MEPI), the US is supporting Ethiopia's efforts to improve the quality of medical training.
Milliard said medical teachers at Addis Ababa University receive incentives to they take additional classes. The initiative has improved the medical school's ratio of books-to-students, from one book per 24 students to one per three.
"Besides [this], we are networking with known US universities through video conferencing so that the students learn from experience of others," he said.
Focus on retention
Challenges also remain in retaining doctors prone to migration. In 2006-2007, 37 percent of the country's public-sector physicians worked in Addis Ababa, which was only home to less than 4 percent of the population.
"The remaining available physicians to the public sector serve the rest of the regions but [are] largely working in major cities," says the government's draft Human Resource for Health Strategic Plan.
One study found that the country faces "a mass exodus of physicians," caused by low salary, insufficient supply of drugs, lack of professional resources and poor management. "Low quality of life in Ethiopia and political repression were found to be the most significant exogenous push factors of migration," the study said.
Ethiopia has been able to increase the number of lower-level healthcare staff, such as health extension workers, helping to bridge the human resource gap at the village level. But in the long run, the ministry said, the present flooding strategy could be the way to boost the public health system.
|
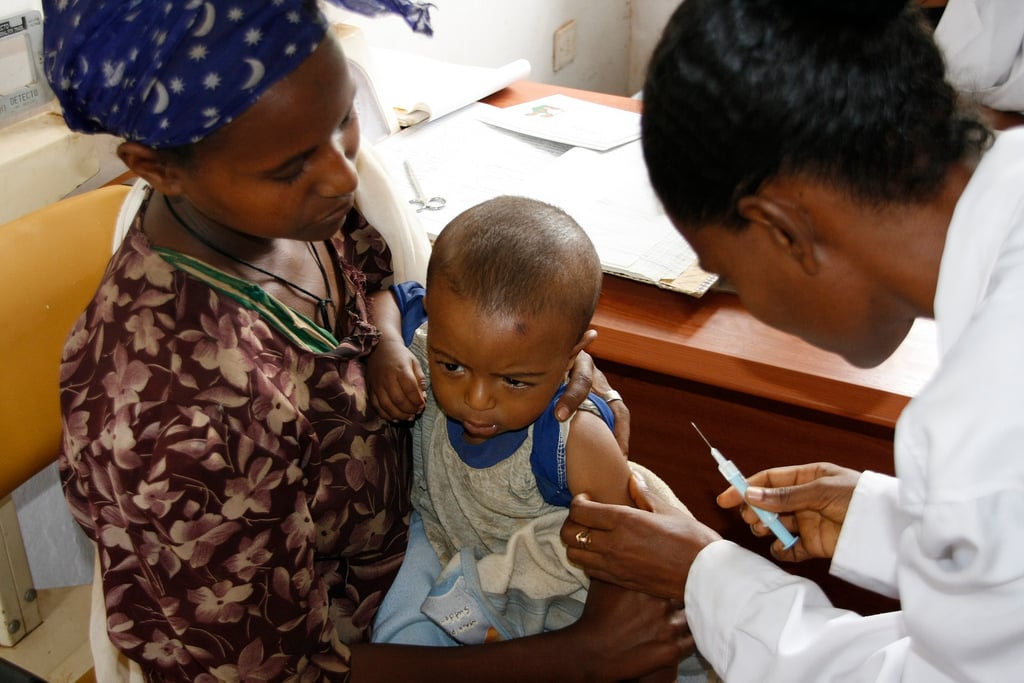
Photo: DFID |
| Child receives her measles vaccination, in Ethiopia's Merawi province |
"But whatever you use to retain should [be] based on what you can offer," Tedros continued. "For instance, you can't compete with developed countries in paying high the salaries. You can't compete with them by using the same approach," he said.
Medical training is expensive, estimated to cost the country an average US$22,745 per student. Doctors are required to serve in public hospitals for some time before going into private practice in different countries.
"Right now we are introducing financial and non-financial incentives to keep them," Tedros continued. "Apart from various incentives that regional governments give, the retention strategy includes lowering the fixed number of years that doctors should serve in rural health facilities and installing private wings in public hospitals," he said.
Accordingly, the government expects graduate medical doctors to serve in rural public hospitals for a minimum of one year, while the service period in public hospitals in major and regional cities might reach up to five years. While in those hospitals, doctors can receive additional financial benefits from private wings set up in public hospitals.
"We have private wing, for instance, that started in Ethiopia [where doctors can] work off-hours and weekends, and they get additional financial benefits," said the minister. "I don't think they would go anywhere because [the income is] not really as high as they would get if they migrate but it's good enough to sustain their life here, and they prefer to stay here with the additional funding they already generating themselves."
Ethiopia currently has no alternative but to train physicians in large numbers, a strategy that has been applied in parts of Asia, said Kebba Omar Jaiteh, a senior WHO expert. "We have seen this trend in India and other Asian countries. When they start training at the beginning, people start moving, but they reach a saturation point whereby…people no longer want to go because the country has improved economic-wise and social-wise. Until that time comes, we need to keep on training in order to serve the people."
bt/aw/rz
This article was produced by IRIN News while it was part of the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Please send queries on copyright or liability to the UN. For more information: https://shop.un.org/rights-permissions